
Augmented Reality offers commercial directors and agencies a powerful opportunity to attract and engage audiences across a variety of media and entertainment verticals. From music and cinema to TV and gaming, immersive integrations can reignite interest, foster deeper connections and open new revenue streams. In social media, AR filters and lenses allow users to transform their appearances and environments. For film and television, activations can provide interactive experiences that extend narratives beyond the screen . In sports, AR overlays deliver stats, replays, and exclusive content that can bolster fan loyalty on and off-site.
As content creation evolves, so does audience interaction—so staying abreast of these changes is crucial. With AR revenue projected to surpass $50 billion in the next three years, we explore what the entertainment industry’s future holds. We’ll also look at how to keep up with this dynamic environment and its top emerging technologies.
Key Takeaways
- Augmented Reality is transforming the entire entertainment sector, from theater, music and cinema to events and television.
- The adoption of AR has introduced novel marketing strategies and revenue streams, such as location-based marketing, interactive advertisements, and brand partnerships.
- With AR’s ability to provide insights into user interactions and preferences, entertainment providers can tailor content and marketing strategies to their audiences more effectively.
- AR has opened new creative opportunities for storytellers and artists, allowing them to craft immersive visual and audio experiences that were previously impossible.
- By enhancing accessibility for those with disabilities and inviting audience participation, AR makes entertainment more inclusive and diverse.
How is Augmented Reality Used in Entertainment & Media?
From filters and lenses on social media apps to interactive marketing and immersive participation in concerts, games, films, and tours, Augmented Reality is quickly expanding its reach in media.
For experiential agencies, product, and content directors, AR also opens up a realm of new creative opportunities to craft unique and memorable experiences. Agencies need to invest in AR technology and skills to stay competitive and offer cutting-edge services—but this investment can simultaneously pay off by deepening consumer-brand engagement. In addition, AR can provide agencies with valuable data on user interactions and preferences, enabling targeted content creation and marketing strategies.
Keep up to date
Sign up to our newsletter for exclusive updates and content, delivered directly to your inbox.
How Has Augmented Reality Evolved in Media and Entertainment Over the Years?
AR first entered the entertainment industry with the help of writer/producer Julie Martin in 1994. Her stage production Dancing in Cyberspace featured acrobats dancing alongside projected virtual objects on the physical stage.
Fast forward a few decades, and AR has evolved into a practical tool for all sorts of everyday applications, particularly when it comes to entertainment—be it media content online, the arts, gaming, or other sectors. With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) forecast at 10.77% between 2024-2028, content creators and experiential agencies that don’t keep up with AR developments risk irrelevance (especially with tech-savvy younger generations, as most AR users fall within the 16 to 34 age group).

AR and VR technology holds boundless potential in entertainment. With constant tech advancements, consumers expect to experience what they love in new and interactive ways, no matter where they are.
How is Augmented Reality Used in Immersive Theater?
Immersive theater removes the traditional barriers between the audience and performers, transforming participants from passive spectators into active contributors to the art and story.
These performance spaces create grand, all-encompassing environments that might include multiple rooms or even an entire building. In addition, immersive theater often employs nonlinear narrative structures, with no clear beginning, middle, or end. This allows audiences to piece together an individual story from their experiences.
Audience members may be invited to interact with the actors or handle props; they can even make choices that influence the outcome of the performance. In this way, each user’s experience is unique, depending on where they are and what they choose to engage with.
How Has AR Changed Immersive Theater?
AR technology would seem like a natural partner for immersive theater, enhancing live performance with digital elements. It can project digital scenery or effects onto physical spaces, elevating visual impacts while foregoing large, physical sets; audience members might also receive additional narrative content or clues to puzzles on their mobile devices or through AR glasses. AR overlays can also enhance inclusivity, providing subtitles, sign language, or audio descriptions for audience members who need them.
Augmented Reality helps immersive theater push the boundaries of storytelling, providing maximally engaging and personalized experiences. It also allows producers to engage demographics who may not have attended otherwise.
Examples of Augmented Reality in Theatre
In March 2020, performance spaces across the UK shut their doors on account of the Covid-19 pandemic—prompting director Toby Coffey to reinvent All Kinds of Limbo as a virtual theater experience. Leveraging immersive technologies, viewer could watch the performance through Augmented Reality on mobile devices, VR headsets, or a standard computer. While vocalist Nubiya Brandon’s performance remained unchanged, the viewing experience varied slightly per device—as if in a real theater.
Since the pandemic, the British theater industry has pioneered similar experiences. The Royal Shakespeare Company’s Dream, for instance—an immersive adaption of the Shakespearean classic A Midsummer Night’s Dream—saw actors perform using motion-capture technology and was accessible through smartphones or computers.
While the viewing experience itself was a free event, audience members also had the option to purchase a ticket that allowed them to interact with the performance in real time. These paying audience members led the lead character, Puck, through the forest—choosing their own routes and interacting with the actors they stumbled upon accordingly. In this way, due to the virtual audience interaction component, no two performances followed the same beat. Dream was, in a sense, AR-enhanced improv.
As RSC director Gregory Doran says, “What’s brilliant about Dream is the innovation at play. An audience member sitting at home influencing the live performance from wherever they are—that’s exciting. It’s not a replacement to being in the space with the performers but it opens up new opportunities […] The story is king, whether you are a gamer, or an audience member. Stories haven’t changed, but the way we engage audiences with them has.”
How is Augmented Reality Used in Music?
Gen Z is the largest generation on Earth currently—so their media consumption patterns are critical to watch and adapt to for success. In particular, Gen Z is made up of avid music consumers: survey data from Edison Research finds that they listen to, on average, an extra 40 minutes more music a day compared to the rest of the population.
Members of Gen Z are also extremely interested in AR. Snap Inc./Deloitte data finds that younger generations are 71% more likely to use AR as a regular part of their life than older generations.

At the confluence of these two generational predilections sits an opportunity to connect. As digital natives, members of Gen Z often want to use technology to enhance and extend their everyday experiences. For example, AR-enhanced album covers and merchandise can enrich touch points by providing access to information or exclusive additional content. Think videos, artist biographies, dance routines, and more. Artist-branded AR apps might also enable fans to remix songs or play virtual instruments.
AR experiences are now often used to promote upcoming albums or singles, offering fans an interactive preview of new music or the chance to engage with the artist’s thematic elements. Augmented Reality can also prove a game changer to reach a global fan base with virtual tours and new release experiences.
Collaborating with 88rising and Microsoft, Rock Paper Reality developed AR and VR experiences for Warren Hue’s album Boy of the Year. Transforming Warren’s distinctive sketches into 3D while preserving his artistic style was crucial, as his fans already loved his designs. Once this world was created, volumetric capture technology was used to virtually insert Warren into the experience. The immersive holographic experience attracted half a million unique visitors.
Let’s chat
Not sure where to start? Book a free strategy call with us to get started! No strings attached.

Augmented Reality in Concerts
AR can be instrumental in promoting live performances and festivals, as well as tapping into new sources of income through virtual concerts. Virtual concerts don’t only allow producers and artists to expand their reach to global audiences—they also significantly reduce event expenses. At the same time, event organizers can increase revenue with marketing opportunities showcased during the event.
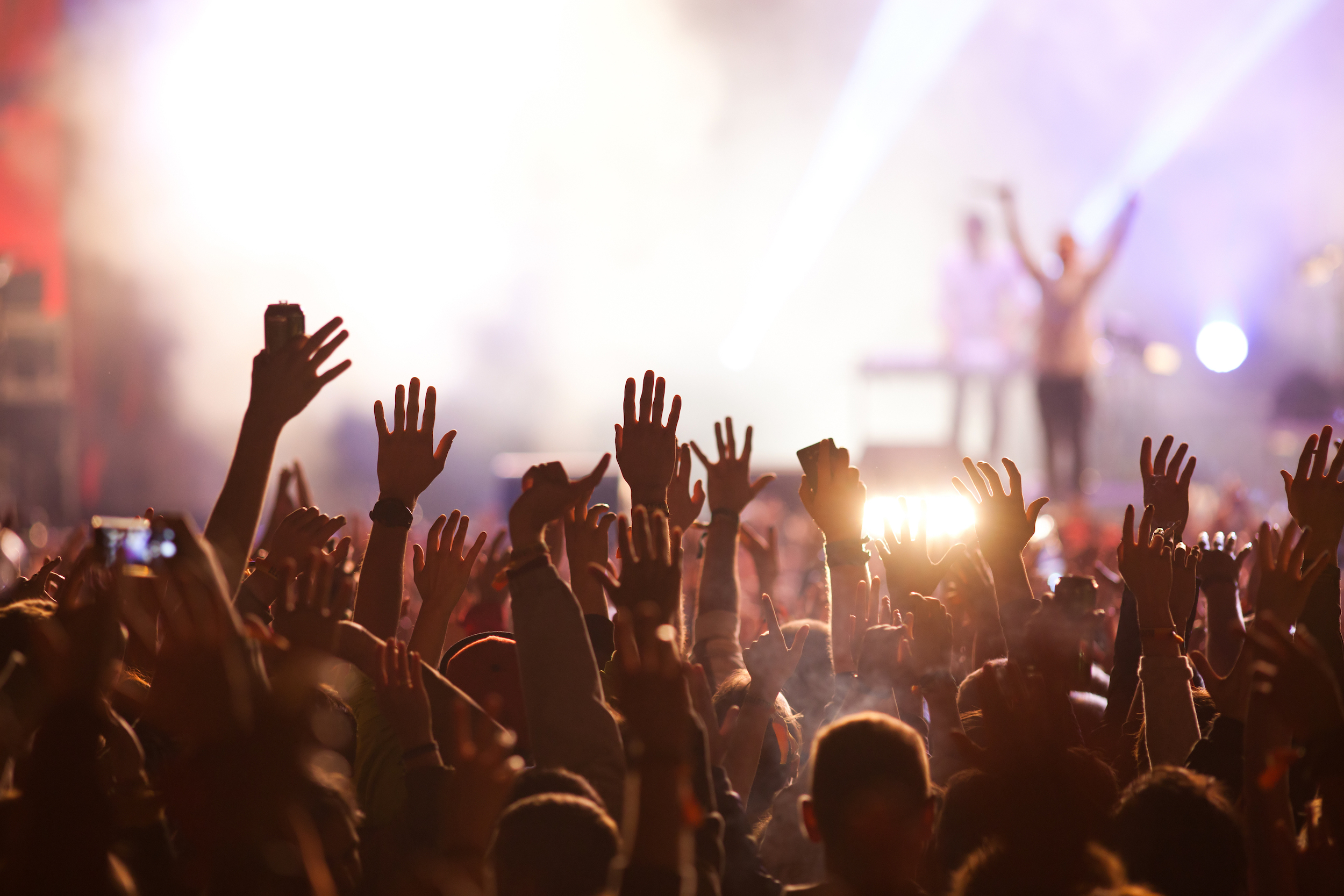

AR apps can enhance live performances with immersive stories behind the music. Some concerts use AR to add a visual layer to live music performances, projecting holographic images onto the stage or even into the audience space. Effects such as virtual fireworks, animated graphics, and interactive light shows can be synchronized with the artist’s performance.
How Can Augmented Reality Revolutionize Music Festivals?
At festivals, AR can provide real-time venue navigation, on-demand performance schedules, and information regarding accommodation and catering. Integrating digital aspects into the experience reduces the cost of printing physical schedules, maps, and information. In addition, it enables a more personalized experience for every festival-goer, increasing satisfaction and encouraging future attendance.
The annual Coachella music festival in California is known for its integration of AR technology into live events. In 2022, on-site and at-home attendees could unlock a new dimension of the event through Coachellaverse, the festival’s own metaverse experience.
The Coachella app allowed users to travel through portals, access immersive Instagram filters, follow navigation and more. Those watching the YouTube livestream online saw a vivid 3D digital show featuring larger-than-life psychedelic images.
As Sam Schoonover, the Innovation Lead for Coachella, points out: “the hybridization of music events through streaming platforms like YouTube is driving tune-in from around the world and bringing at-home and on-site audiences closer together in the process. For these reasons, we believe that Live AR will enable a massive evolution in performance visuals over the next few years.”
What is Immersive Audio?
Instead of superimposing visual content onto the user’s environment, immersive audio overlays digital audio onto the physical soundscape. Through spatial audio technology, sounds can be positioned within a three-dimensional space for a highly immersive auditory experience.
Immersive audio typically requires a device capable of delivering spatial audio, such as specialized headphones or earbuds. It may also rely on head tracking and other sensors, to adjust the experience based on a user’s movements.
Background sounds at a venue can be augmented with immersive audio to match the theme of the event. Attendees can experience music that seems to come from different directions or parts of a venue, creating a lush auditory soundscape. In the case of virtual or hybrid events, immersive audio can recreate the sense of being at a live venue. It provides at-home listeners with a spatial audio experience that mimics sounds they would hear if physically present.
For individuals with visual impairments, immersive audio can provide spatial cues about their environment, aiding in navigation and interaction with surroundings. It also provides users with verbal turn-by-turn directions or contextual information.
Augmented Reality in Cinema and Movies
Envision attending a movie where, without 3D glasses, the film experience becomes immersive. With an AR activations, characters could seemingly walk alongside you in the theater and action scenes could spill into your space. At the latest sci-fi hit, the ceiling above may transform into a cosmic panorama of galaxies, stars, and planets. Immersive enhancements have the potential to redefine the boundaries between narrative and viewer, creating exciting experiences and new revenue opportunities.
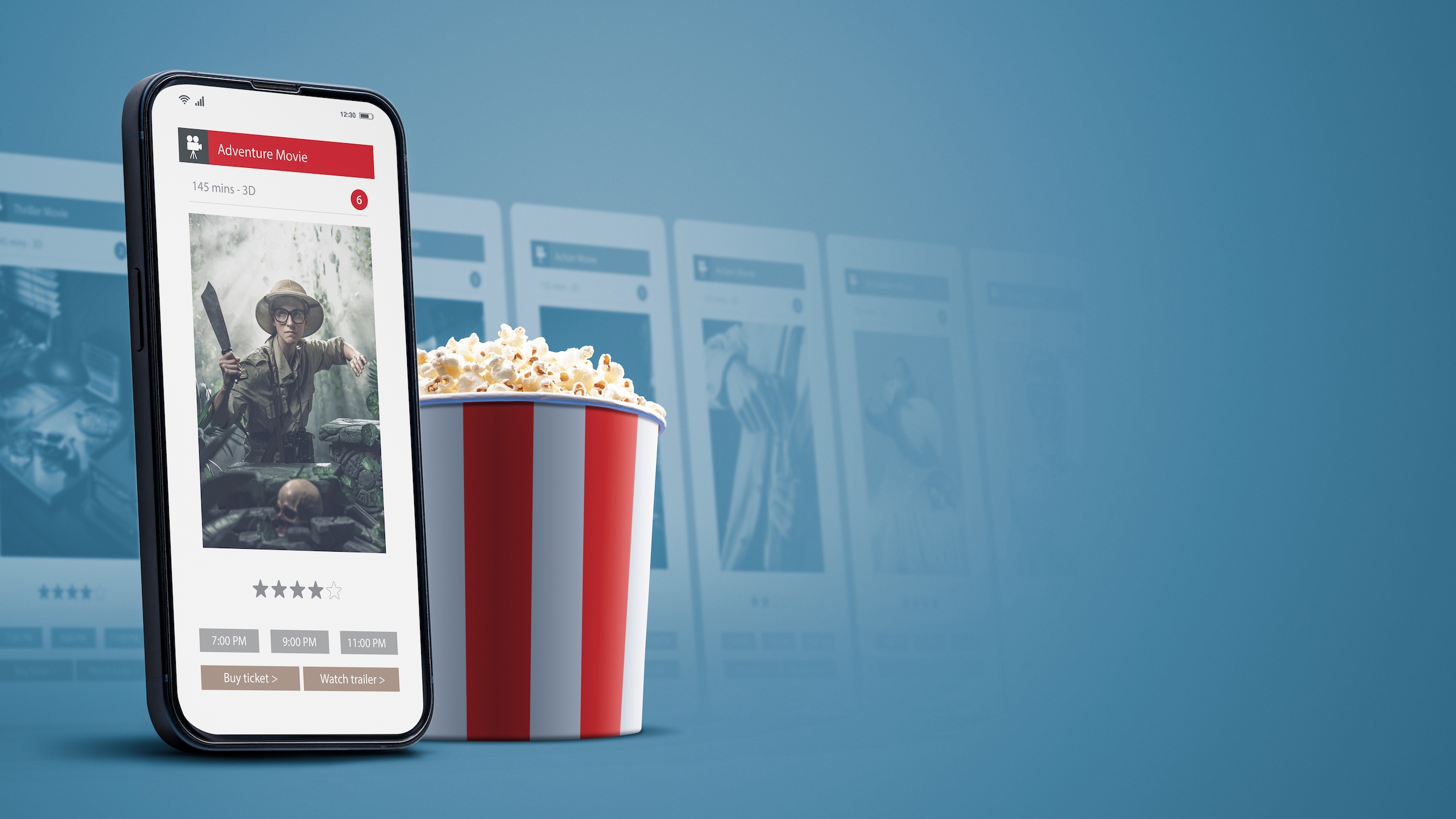
Interactive Movie Posters and Marketing
From the initial marketing stage, viewers can scan movie posters with their smartphones to unlock exclusive content. This might include trailers, behind-the-scenes footage, or interactive elements related to the film. Some trailers include AR elements that activate when viewed through certain apps or AR glasses. These elements add a new layer of immersion to the preview experience. They can also encourage users to explore releases they may otherwise have missed.
Before the film, audiences can participate in AR experiences in an interactive lobby or from their seats. Moviegoers might engage with AR games, photo opportunities, or information related to the film and characters. This presents unmissable opportunities for creative and experiential directors, who can monetize digital spaces with advertising, partnerships and placements.
Augmented Reality is also trickling into home cinema. In 2022, Disney+ released its first AR-enabled short film, Remembering. To download the Remembering: The AR Experience app, viewers scan a QR code on their TV screen. The AR app then runs alongside the movie, telling viewers when to aim their phones at the TV. This triggers AR displays, which feature dolphins, butterflies, and luminous flora (among other virtual elements) in the viewer’s the room.
How Can Augmented Reality Be Used at Events?
AR is transforming event experiences by offering immersive and interactive opportunities. From virtual product demonstrations to engaging presentations, AR can captivate audiences, provide personalized content, and create more memorable interactions.
Augmented Event Spaces and Venues
Augmented event spaces and venues offer immersive experiences that engage attendees, enable interactive storytelling, and facilitate navigation. They also allow for cost-effective setups, minimizing physical logistics while maximizing impact. Brands can leverage AR to provide memorable, personalized content that resonates with participants.
The Globo Rio app, designed for the Rio Olympics, showcased the large-scale application of AR at event venues. It utilized Geo AR to serve as a user-friendly, interactive guide for the Olympic Village. With Augmented Reality, users could effortlessly navigate venues, access schedules, statistics, and track live results. Its versatility and user-friendliness were critical for the event, garnering over 100,000 downloads within the first 48 hours.
In a similar vein, Rock paper Reality created a gamified AR experience for an exclusive Amazon Prime event. Used by 70% of guests, the activation guided traffic around the venue and incentivized users to discover content about the exhibits on display. This included exclusive information, fun facts and behind-the-scenes details.
AR Experiences at Conferences and Trade Shows
Hosting trade shows for large products can be expensive, given the need for vast spaces to display them. However, imagine the possibilities of showcasing a range of large items virtually. Picture a station where you can view a life-size 3D car model, or visualize manufacturing equipment functioning in front of you. These technological advances enable attendees to interact with products in unprecedented ways, all without the high costs of physical venue rental.
Hino Trucks USA developed realistic 3D models of their top-grade vehicles and engines for trade show viewing. By scanning a QR code, trade show visitors could explore the models in AR. This innovative approach reduced transportation and logistical challenges, required less exhibition space, and allowed Hino Trucks to showcase their entire fleet at trade shows cost-effectively and with ease.
This resulted in significant savings for the company while providing customers with an easier way to understand complex products.
Rock Paper Reality created an AR visualization tool for clean energy provider Rondo Energy. It enabled prospects, stakeholders and team members to understand the inner workings of its cutting-edge Heat Battery and was used both at trade shows and on-site.
How is Augmented Reality Used in Gaming?
Augmented Reality in PC and mobile gaming is not just an enjoyable pastime. Rather, it is a paradigm that expands the boundaries of interactive entertainment. Approximately one-third of Americans are interested in playing AR games, significantly outpacing interest in other uses of AR by nearly threefold.
Augmented Reality in Mobile Gaming
Mobile gaming has particularly benefited from AR due to the ubiquity and increasing power of smartphones. AR mobile games leverage a device’s camera, gyroscope, and GPS to provide an engaging gaming experience directly on the phone.
These devices capture the player’s environment and superimpose digital game elements onto it. For example, Augmented Reality mobile games might allow players to race cars on virtual tracks laid over their kitchen tables, or defend against alien invasions in their backyard. The portability of mobile devices makes AR games accessible at any location—turning mundane spaces into exciting arenas.
Games such as Pokémon GO have exhibited the potential of AR in gaming. In this groundbreaking entry to the Pokémon franchise, players use their smartphones to search for and capture virtual creatures that appear in their real-world surroundings. The game uses GPS to track locations, making the gameplay experience unique to each player’s movement.
Advantages of Augmented Reality in Gaming
AR games offer a unique and captivating experience with opportunities to play outside, socialize, and get active. In addition, users can engage with just a mobile phone—they don’t need to invest in expensive gaming equipment.
Beyond in-app purchases and advertising, AR games offer marketing opportunities to feature products within the game environment. Additionally, by combining physical locations with digital gameplay, AR games can drive foot traffic to businesses and landmarks. This opens possibilities for collaboration between game developers and local businesses, offering promotional deals and benefits for both parties. Pokémon GO takes great advantage of such partnerships, hosting “gyms”—arenas for players to face off against one another—at prominent local landmarks and businesses world-over.
AR games that require players to move through real-world locations can also provide developers with data about behavior, preferences, and patterns. This information can improve game design, user experience, and targeted marketing efforts.
Augmented Reality in TV
When it comes to television, AR allows for a more immersive storytelling experience by adding layers of visual depth and context to the narrative. This can be particularly impactful in documentaries, educational programming, or even live sports, where additional information about players or historical context can be displayed in a compelling visual format.
While watching TV, viewers can use a tablet or smartphone to access AR content. This might include interactive games, social media streams, or behind-the-scenes info—all potentially increasing viewer retention and loyalty.

Take for example, the reality television show The Circle. The series features contestants who must avoid physical contact and can only interact via a social media platform. They establish connections, deceive others as catfish, and use their charisma to compete for a $100,000 prize. In the earlier seasons, the creators incorporated Augmented Reality (AR) to enable viewers to unlock additional content.
AR enables content owners to offer innovative and immersive advertising formats. Advertisers might pay a premium for AR spots that showcase their products in a 3D space, or integrate them into the content in a way that traditional commercials cannot. This increases the value of advertising space and can open up new revenue streams.
What is the Future of Augmented Reality in Entertainment & Media?
AR’s ability to engage audiences on an interactive, personalized, and inclusive level has opened new creative horizons for content creators—and new marketing and revenue opportunities for industry stakeholders. As AR continues to mature, its integration across various entertainment mediums is poised to redefine the audience experience. This makes for an exciting time for both consumers and innovators in the world of media and entertainment.
Rock Paper Reality (RPR) empowers brands to provide extraordinary entertainment experiences. Our award-winning team of strategists, designers, creators, and engineers specialize in innovating, developing, and deploying immersive experiences. Let’s bring your vision to life—get in touch.

Frequently Asked Questions on Augmented Reality in Entertainment & Media
What Challenges and Opportunities Does AR Present for Content Creators in Entertainment and Media?
AR presents content creators with the challenge of mastering complex new tools and storytelling techniques. Simultaneously, it offers vast opportunities to engage audiences more deeply, create interactive narratives, and tap into innovative monetization strategies.
What Trends Are Emerging in the Integration of AR Across Entertainment and Media Platforms?
Trends include the use of interactive advertising, and the rise of virtual live events that blend physical and digital experiences. Additionally, there’s an increasing focus on personalization and accessibility. This allows for tailored content that reaches a broader audience, including those with disabilities.
In What Ways Are Streaming Platforms Integrating AR Features to Enhance User Engagement?
Streaming platforms can integrate interactive filters, real-time effects during live streams, and immersive content that overlays digital assets into viewers’ environments. This can increase user engagement by enhancing interactivity and personalizing viewing experiences.
