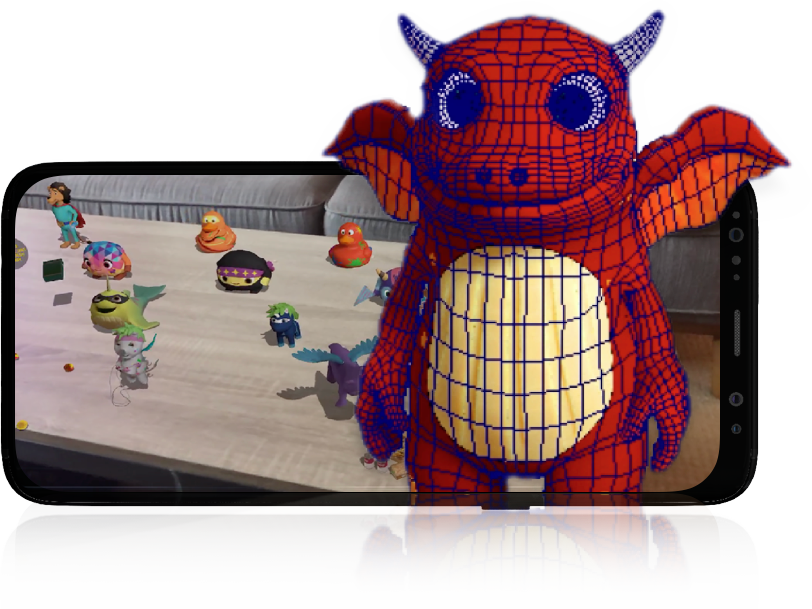
Here’s how to level up your brand’s marketing with 3D video production
Leave a CommentAre you investing in immersive experiences or digital content like games, but struggling to get enough reach? You owe it to yourself to promote your experiences with high quality 3D video production that generates excitement and reaches a larger audience. You’ve probably already created the 3D assets anyway – so why not get more use out of them?
The number one mistake we see digital marketing teams making is that they build an engaging and impactful immersive or digital experience – but then they don’t promote it. After all that effort of building the experience, brands are all too often left wondering why it didn’t have the impact they wanted.
Take Pokémon Go, the most successful AR game of all time. A major factor in the game’s success was an irresistible launch video, which has generated 48.6 million views to date. Sure, when fans have downloaded your game you can win them over with impactful gameplay – but first you have to get people in the door. A promotional video is by far the best way to reach audiences and establish awareness, and a 3D-animated video is the best of the best.
Key Takeaways:
- Why choose 3D animated video over traditional filming? Whether it’s ultra-realistic product showcases or entirely virtual brand worlds, high-quality 3D video production gives you the control you need to bring your vision to life without creative boundaries. It also gives you the building blocks to create variations with ease across regions or for different campaigns. Don’t like that tree there? Just move it!
- Extend Your Reach: if you’re building a game or an immersive experience, you have to promote it with a compelling video or you will be disappointed with your metrics. There’s a reason the film industry spends as much on marketing as they do on the production itself! 3D video production allows you to take the digital assets from your experience and use them to create a video that can be shared across channels and consumed easily to extend your reach and generate excitement.
- Creative Flexibility: With 3D design software and real-time game engines, there are no creative limitations when it comes to showcasing your brand in unique and surprising ways. From gravity-defying experiences to imaginative worlds, 3D video production expands your storytelling capabilities.
- Reusability & Cost Efficiency: Your existing 3D assets can be repurposed for 3D animation videos and reused across multiple projects, reducing costs and speeding up production without sacrificing content quality.
- Key Benefits: Brands that integrate 3D animation videos into their marketing strategy can expect higher engagement, boosted conversion rates, a stronger appeal to younger, tech-savvy generations, and enhanced organic reach by creating highly shareable videos for social media.
- AI Impact: Generative AI is rapidly evolving in this space and presents an exciting future to reduce the cost and complexity of creating high quality 3D video production. However, today it is still exploratory and doesn’t give producers the necessary control to achieve their exact vision.

This is why quality 3D video production should be an essential part of your toolkit
When you showcase your experience with a showstopping 3D video, you give your promotion an extra dimension. Attention spans are down to the length of a TikTok video, but 3D animation video pops off the screen, grabs eyeballs and doesn’t let go. When you want your brand content to stop viewers scrolling, 3D video does the job.
Using tools like Unreal engine, Blender and innovative AI automation, 3D video production studios create characters and worlds that hook viewers and make them want to dive deeper. Want to defy gravity? Animate objects that shape-shift in mid-air? Take customers to a whole new planet to meet an animated brand ambassador that talks to you like they’re real? Working with a 3D animation studio like Rock Paper Reality, the only limit is your imagination.
This creative flexibility allows your brand to stand out, be playful, and surprise your audience. A 3D promotional video doesn’t just tell your audience something – it makes them feel something. That emotional connection is what draws people into the experience you’ve created, turning viewers into customers.
By investing in premium video production, you don’t just create cool videos: you future-proof your marketing. We’re living in the age of AR (Augmented Reality), VR (Virtual Reality), and XR (Extended Reality). Brands need to adapt and invest, as audiences – especially younger people – want the kind of interactivity that cutting-edge computer-generated imagery (CGI) gives them: 77% of Gen Z want personalized and customized brand interactions which anticipates what they might want to do next. And when they love it, they talk about it: 76% of users will recommend a brand that provides an exceptional digital experience, which means your innovation turns people into customers and brand advocates sending your content viral.
So, if you’re planning to launch a game or a digital experience, you’ll want to think about a strategy for high-quality 3D animated marketing videos. We’re dogfooding this at Rock Paper Reality by creating a promotional video for Defenderella, a Mixed Reality game we recently developed in-house. You can see how something like this would generate excitement without the user ever needing to put on a headset, download the game, and try it themselves.
The Benefits of 3D Content
Choosing a wine is more than just wondering what pairs well with fish. That’s why winemaker Chronic Cellars partnered with Rock Paper Reality to hook their customers with an AR experience starring a 3D animated sommelier based on artwork from one of the company’s bottles. This custom-made digital brand ambassador was created using cutting edge 3D modelling, CGI animation and AI tools – all assets that could be shown off in the promotional push to get users into the AR app.
The work that goes into creating engaging characters like this sunglasses-wearing skeleton goes to waste if you don’t convince customers to actually click on the experience. Avoid losing customers by promoting your experience with images and video that grab attention, and you draw viewers from the video to a far more engaging and interactive experience.
To bring viewers to the point where they could actually try out the Chronic Cellars AI avatar, Rock Paper Reality took the 3D assets that were already built for the character, built a new scene in Unreal Engine, and rendered out a photorealistic video to promote the experience.
3D assets used for rendering a 3D video
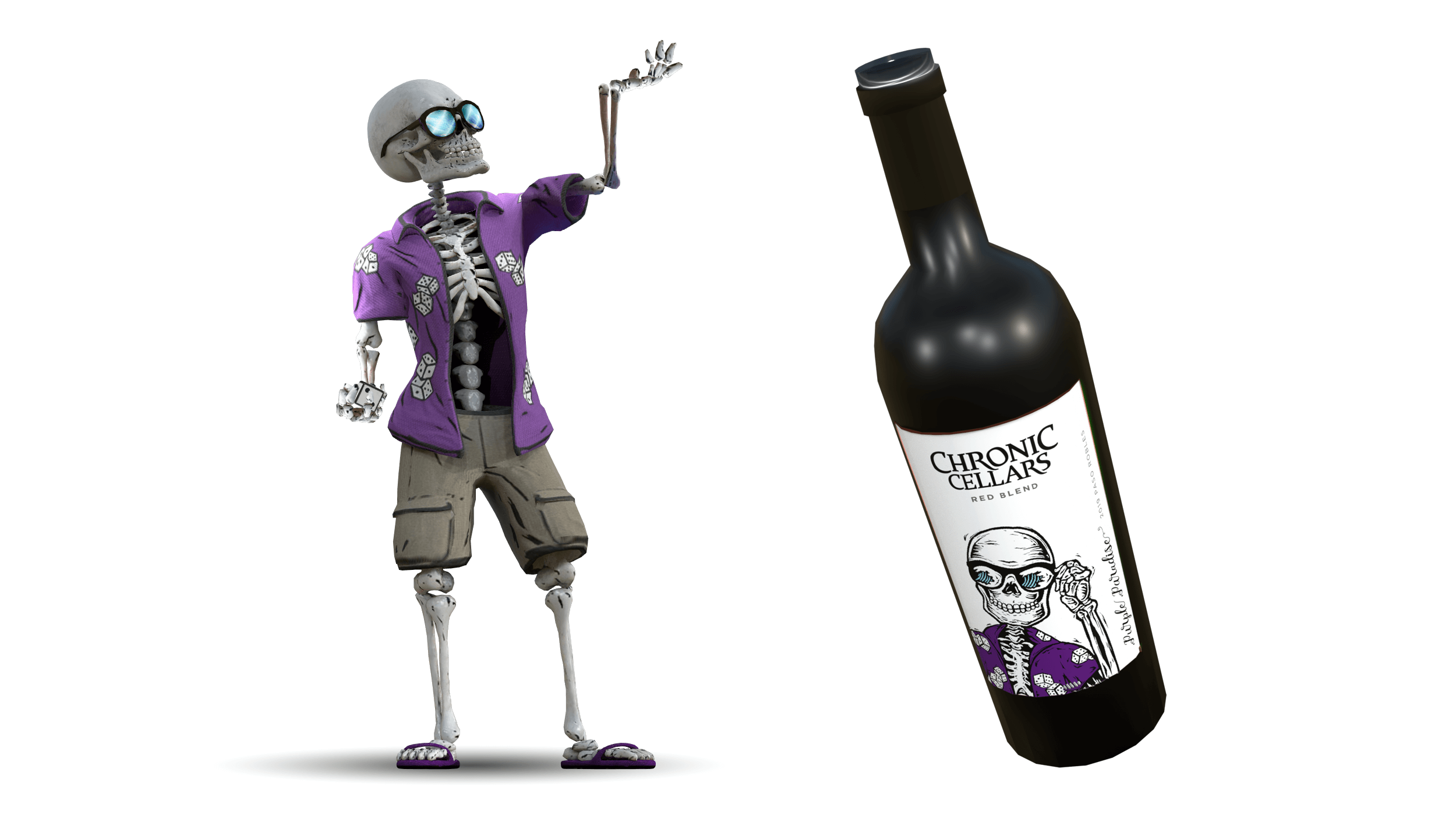
This is how partnering with a 3D animation video production company unlocks a crucial first impression that makes a customer feel they can’t miss out on your experience.
Here are the key benefits of 3D video marketing:
Realism and Immersion
CGI 3D video achieves a level of realism on a whole other level compared to 2D animation or motion graphics. Lifelike textures, sophisticated lighting and welcoming environments make your video more immersive and enjoyable. 3D modelling animates fluid dynamics, particle effects and physics-based interactions realistically. And advanced lighting systems mimic real-world physics, enabling soft shadows, reflections and refractions and atmospheric effects that add to the believability of a scene.
But realism is only the start. 3D animation video allows you to take customers on any incredible journey you can imagine, to fantasy worlds and hyper-stylized experiences. Look at this Airbnb advert which turns Paris into a pop-up book.
With the extra dimension of fully rendered environments, you can employ camera movements like tracking and zooming for that cinematic style – and your camera can fly literally anywhere. You can even combine jaw-dropping realism with eye-popping fantasy, like this CGI advert that blends art with the real world to tell a mesmerizing story about Coca Cola.
Powerful Product Showcase
3D product animation is ideal for any product design or entertainment project where realism leads to engagement – and conversion. Emotional connection is more than audiences having warm and fuzzy feelings about your brand: eye-popping adverts mean increased ad revenue, and innovative product showcases boost conversion rates. According to Shopify, 360-degree product animations can increase conversions by up to 250 percent.
3D modelling showcases your products from every angle, in any environment, making them look as epic as they deserve. Many innovative retail brands like Nike or IKEA have replaced much of their product photoshoots with virtual photography, because once you create a 3D asset you can create almost endless variations of colors, backgrounds and angles with a few clicks. This reduces your costs when localizing your product marketing assets for any region. Most importantly, a 3D-rendered product video means viewers see a product showcased in creative and enticing ways that simply aren’t possible – or are prohibitively expensive – for conventional filming.
Flexibility and Reusability
When you create a 3D asset, it can be dropped into any environment and viewed from any angle. That means the models, textures and animations you’ve already made can be reused across multiple projects or adapted for different scenes without having to start from scratch. You can scale the same asset up for cinematic-quality visuals in film, games and high-budget advert, or scale down for mobile-friendly content that still looks polished. This makes 3D content more versatile and cost-effective in the long run.
Once you’ve invested in developing your 3D assets for your interactive AR, VR and immersive web applications, why not get more use out of them? Make a 3D video using those same assets, and you can activate additional channels and reach a wider range of platforms to promote your immersive content.
Manchester City made a web-based escape room game and repurposed those assets to create a marketing video that extended the reach of their campaign and attracted more users to try out the game.
Wow Factor
Here’s the bottom line: CGI 3D animation inherently has a “wow” factor. A jaw-dropping video brings a level of sophistication that hooks a viewer’s attention and leaves a lasting impression compared to conventional filming, traditional 2D animation or motion graphics. Check out this advert for Tectrol, for example, which presents important stats and information while hooking viewers with animation that zooms into space and back to a tree blossoming from a phone screen.
For younger viewers, at Halloween we launched our Final Selfie branded GenAI filter, fully configured into a web-based augmented reality (WebAR) experience designed to turn fabulous boys and ghouls into shareable spooky images. To generate excitement for the experience, we created a short 3D video for social that leaves users wanting to try out the AI face filter experience.
Key Challenges in Modern Storytelling
The online marketing landscape evolves fast. Whether the goal is to engage younger audiences or stay ahead of technological trends, brands must continually innovate to thrive. But the good news is that despite the challenges and pain points in this space, there are huge opportunities to get tangible results.
Here’s how premium 3D video tackles some of the biggest challenges brands face right now:

Production Costs
Traditional video production can be expensive and resource-intensive to set up a physical shoot with actors, props and permits. Depending on your product and industry, real-time 3D video production could be a more cost-effective alternative – and could even give higher quality results. When a physical product is the star of the show, we see the highest ROI for brands with high-value products like automotive, industrial, or luxury goods that are costly to work with on a commercial shoot. A 3D animation video production company with experience of working alongside global brands already has the streamlined processes to optimize your budget.
The Solution: Lean Production Techniques
A 3D animation studio has the expertise and the toolkit to deploy tools like AI-powered video editing and virtual production for content that reduces costs without compromising quality. Most importantly, a repeatable, streamlined workflow is capable of scaling up your premium content creation.
Asset Creation
Brands often have access to great storytelling and creative assets, but can’t always deploy those assets to their full potential. With a bit of planning, however, brands can reuse those assets and repurpose content – reducing costs and opening up new avenues.
The Solution: Effective Asset Repurposing
Once you’ve invested in creating a 3D model of your product or environment, you can reuse it again and again. Need a new ad? Don’t drag an army of people into a studio to film a new ad. Just take your 3D assets, change the lighting, adjust the angles or drop your product into a new background. Boom! Fresh content, with far less effort (or cost) than starting from scratch.
That means creating digital assets which can be quickly altered and re-used across campaigns and platforms, and implementing processes that make it easier to do so. The initial cost of a reusable model may be higher than throwing together a single-use asset, but you can use it again and again, saving time and money when you do. Our Final Selfie Halloween project is a great example: once we built what we needed for the AR experience, we were able to also create a 3D promo video from the same assets to attract more users to try it out.
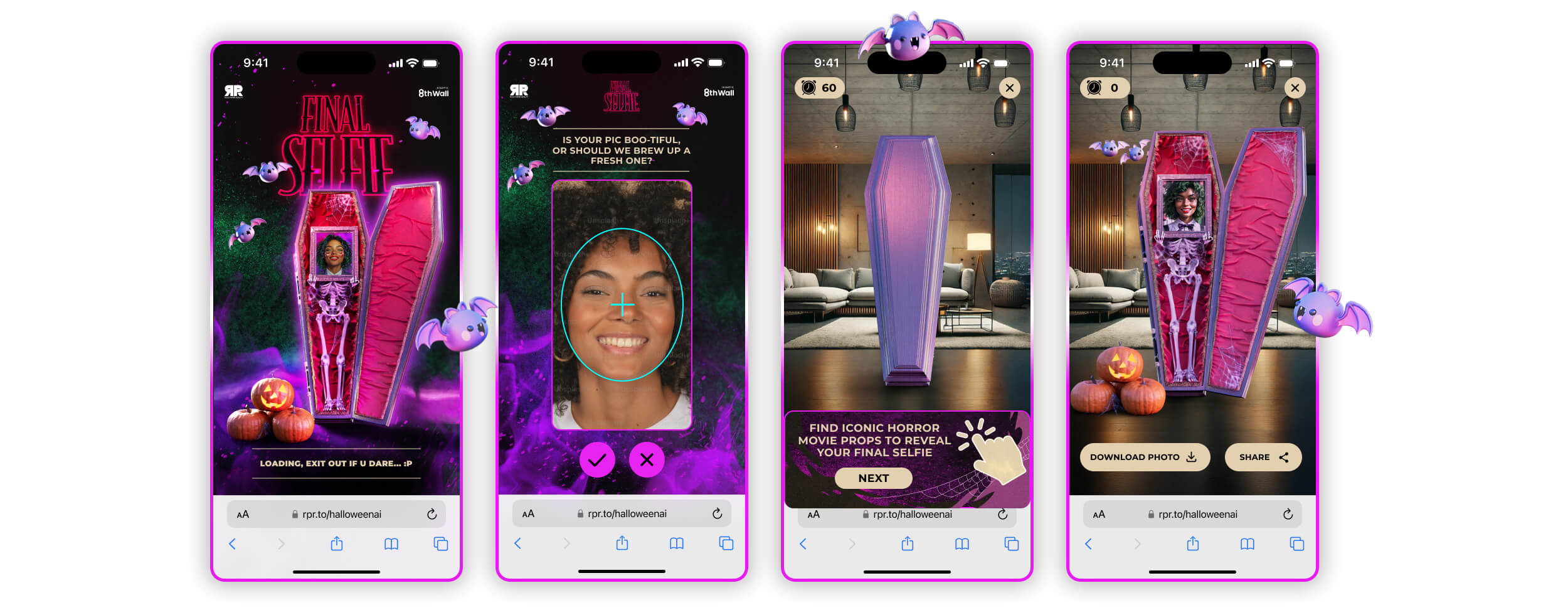
This is how the Final Selfie experience looked, featuring the assets we utilized for the 3D promo video.
Engaging Younger Audiences
Gen Z are extremely visually savvy. These younger demographics demand dynamic digital-first experiences that “pepper in a personal touch”, according to Forbes. The popularity of TikTok and Instagram show how static and conventional approaches might fail to hold their interest.

The solution: Targeted Visuals for Younger Audiences
Create dynamic short-form content tailored to platforms like TikTok and Instagram, emphasizing authentic connection, storytelling and interactivity. The right mix of creativity and relatability can even transform content into a viral phenomenon, as share-worthy elements like humor, awe or usefulness organically amplify your reach.
Simplifying Complex Concepts
It can be a struggle to distill intricate products, services or ideas into simple, visually engaging representations that resonate with audiences.
The solution: Visual simplification tools
Invest in 3D video animation services that turn complex concepts into intuitive and engaging content, such as interactive infographics or animated explainer videos.
Staying Ahead of the Curve
Technology can do cool new things every day, which means brands need to stay nimble. A slow decision-making or production process can cost your brand when rivals do something cutting edge and cool while you’re still figuring out the technicalities or debating the cost.

The Solution: Future-proof Your Process
Positioning as a forward-thinking, innovative brand is key to differentiation, and achieving this requires quick thinking to deliver consistent and creative execution across all platforms. The smart play is to invest in flexible, future-proofed content creation tools so you can jump onto new trends and experiment with new formats.
Consumers love storytelling that evokes emotion. With the immersive experience sector projected to reach approximately $250.96 billion by 2034, you can’t afford to be left behind. When you create your immersive experience, make sure viewers see it and want to be part of it.
What Can a 3D Studio Like Rock Paper Reality Do For You?
Rock Paper Reality helps clients realize those imaginative and attention-grabbing visuals. We’re a full-service 3D video production powerhouse, and we do it all: modeling, customizing, animating and rendering to deliver high-impact 3D videos.
Here’s how we do it:
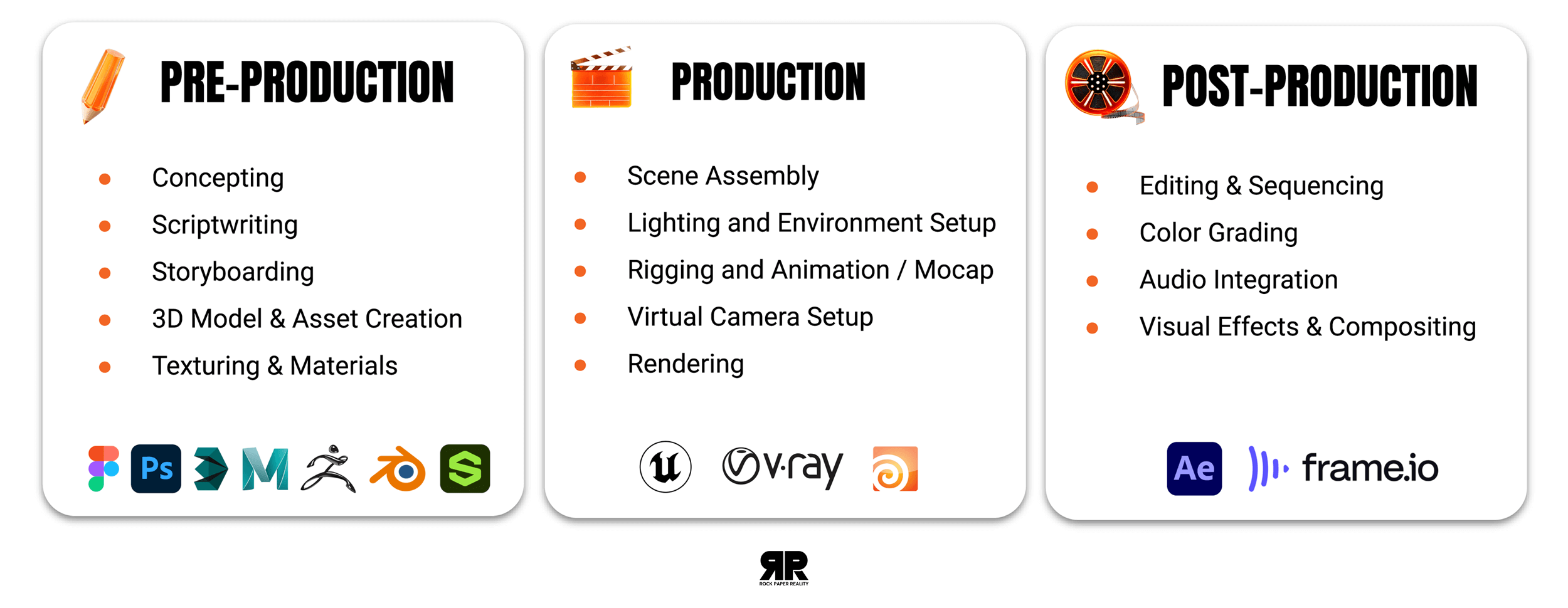
What are the Benefits of a 3D Animation Studio Like Rock Paper Reality?
Rapid production timelines: Creating or utilizing existing brand 3D assets, modelling and real-time rendering to produce high-quality 3D videos in no time.
Storytelling and marketing campaigns: Delivering visually stunning, engaging and memorable content.
We take the high-quality 3D assets developed for the experience and composite them onto video to create a VFX marketing video that helps promote the experience and tell the story.
How Will AI Video Disrupt Premium Video Production?
Let’s take a second to talk about AI. Generative AI video technology is revolutionizing premium video production, making it faster, more accessible and more innovative. Naturally, some creators and brands are wondering why they can’t do all this themselves. Unfortunately, AI video generators are still in their infancy and lack the fine tune control you need for a finished product. It’s great for concepting, but the content it generates is limited in ways which could put viewers off – or worse, seriously damage your brand.
That said, AI clearly has transformative potential, and video production companies are busy integrating the latest tools. By automating complex processes, enhancing creative capabilities, and democratizing access to efficient tools, AI is set to play a huge role in the landscape of premium content creation.
Here’s how:
Enhanced Creative Freedom
Tools like Sora or Runway enable creators to quickly experiment with animation styles, effects and techniques that were previously labor-intensive or just impossible. With these tools available, you can speed up ideation and planning and quickly get a first look at concepts, storyboards and pre-visualization animatics.
Made with Sora
Cost Reduction and Efficiency Gains
AI video production can lower costs by automating time-intensive tasks like editing, rendering and effects creation. Using AI tools such as Runway and Pictory, we can automate video editing, apply filters and potentially slash production timelines. Creators using AI can also speed up the processing of multiple versions of a video tailored to specific demographics, preferences or platforms.
Virtual Production
AI can generate photorealistic virtual environments and characters, reducing the need for physical sets or extensive location shoots. For example, an AI tool could replace traditional green screens with real-time background replacement.. AI-driven engines like Unreal Engine render high-quality visuals in real-time, merging production and post-production.
Deepfakes
A huge amount of video content is centered around a person speaking. Think about news reporting, influencers or instructional videos which brands invest a lot of time in creating. AI tools like Synthesia can be used to generate deepfake-style videos without the need for actors or expensive shoots, so you can scale up your content creation.
Ethical Considerations and Disruption
While these powerful tools have a lot of benefits, there are some challenges and ethical considerations before adopting AI video production:
Job Displacement: Though it creates opportunities for AI-specialized talent, automating tasks like editing and VFX might reduce demand for some jobs done by humans.
Ethical Concerns: AI-generated deepfakes and synthetic media raise concerns about authenticity and misuse, particularly in advertising or branded content. Brands, staff and content creators need to be aware of potential damage to their brand, not to mention the potential impact on wider society.
The Future of Brand Storytelling
The demand for dynamic, emotionally resonant and technologically advanced content is exploding, especially among Gen Z audiences. Attention is fleeting and competition is fierce – so make sure you wow viewers with promotion that’ll hook them in to try your experience.
And whether you’re taking them on a roller coaster ride through an eye-popping animated world or showcasing a product’s journey from concept to reality, 3D video makes stories more immersive, engaging and unforgettable.
Partnering with an immersive storytelling agency like Rock Paper Reality unlocks the creative potential of 3D video and provides the best possible spotlight for your brand. Before your brand gets left behind, contact us now and talk us through your goals to see what Rock Paper Reality can do for you.
FAQs about 3D Video Production
What is 3D video production, and how does it differ from 2D video production?
3D video production involves creating animations or video content in three-dimensional space, giving depth, perspective and realism to objects and scenes. Unlike 2D production, which creates flat visuals, 3D allows for the rotation, scaling and movement of objects in a way that mimics real-world physics.
What industries benefit the most from 3D video production?
Industries that can use 3D animation include:
Advertising and Marketing: Immersive experiences, product showcases and dynamic visuals.
Entertainment: Movies, gaming, and virtual reality experiences.
Architecture and Real Estate: 3D walkthroughs and visualizations of buildings.
Healthcare: Medical simulations and training.
E-commerce: 3D product models to enhance online shopping.
Education: Interactive learning tools and visual aids.
What tools and software are commonly used in 3D video production?
Common 3D production tools include:
Modeling and Animation: Blender, Autodesk Maya, 3ds Max, Cinema 4D.
Rendering: V-Ray, Arnold, Redshift, Unreal Engine.
Texturing: Substance Painter, Mari.
Motion Capture: MotionBuilder, Move.ai.
Compositing: Adobe After Effects, Nuke.
Game Engines: Unity, Unreal Engine.
How long does it take to produce a 3D video?
Production time depends on the complexity and length of the project. The key stages include modeling, rigging, animating, texturing, rendering and compositing. A simple 3D animation might take a few days or weeks, while a high-quality 3-minute video or a fully immersive experience with complex characters, environments and effects could take several months. When time is a factor, expert 3D production facilities like Rock Paper Reality have the streamlined process, automated tools and know-how to get it done in the timescale that works for you.
What are the main cost factors involved in 3D video production?
Key cost factors include:
Number of Custom Assets: Custom environments and assets all need to be modelled, textured, and rigged up for animation.
Complexity of Assets: Detailed models and textures require more time and resources.
Animation Quality: Realistic character movements or simulations increase costs.
Rendering Time: Real-time rendering engines like Unreal Engine drastically reduce the render time that might be needed with software like V-Ray or Arnold. Team Size: Costs increase with the number of animators, designers, and technical specialists needed.
Software and Tools: Licensing fees for professional 3D software.
It’s important to think of 3D assets as investments which can be used again.
Can 3D assets be reused or repurposed for other projects?
Yes! One of the major advantages of 3D video production is the ability to reuse and repurpose assets. Models, textures, animations and environments can be adapted for new projects, saving time and costs in the long run. For example, a 3D model used in a commercial can be reused in a game or interactive web experience.
What are the challenges of 3D video production?
Common challenges include:
Time-Intensive Process: Each step, from modeling to rendering, can be lengthy.
Costs: Quality production requires skilled professionals, powerful hardware, and licensed software.
Technical Complexity: Rigging, simulations, and lighting can be challenging.
Rendering Times: High-quality outputs can take hours or even days to render.
Steep Learning Curve: Mastering 3D tools and techniques requires training and experience.
This is why the smart play is to partner with a production studio like Rock Paper Reality which already has the tools and experience to deliver you what you need in a cost-effective way.
How do you ensure 3D video content looks realistic?
Realism in 3D production can be achieved through:
Detailed Modeling: Creating intricate and accurate models.
High-Quality Textures: Using detailed, high-resolution textures.
Advanced Lighting: Implementing realistic lighting and shadow techniques (e.g., global illumination, ray tracing).
Physics Simulations: Adding real-world physics for movement, water, fire, or cloth.
Post-Processing: Applying effects like depth of field, motion blur, and color grading during compositing.
What is the role of rendering in 3D video production?
Rendering is the process of simulating lighting in a scene with 3D models and animations to produce a final 2D video or image. It combines all elements, such as textures, lighting, shadows, reflections, and effects to produce the finished product. Rendering can be resource-intensive and time-consuming, especially when aiming for high realism, but techniques like real-time rendering, cloud rendering, and GPU-based rendering help speed up the process.
How is AI affecting the 3D video production process?
AI is transforming 3D video production by:
Automating Tasks: AI tools assist with modeling, rigging, and texturing.
Reducing Render Times: AI-accelerated rendering engines optimize performance.
Simplifying inputs: AI can generate procedural environments or animations based on simple prompts.
Improving Realism: AI-powered tools can enhance details like facial animation or physics simulations.
Simplifying Motion Capture: AI can capture motion data without expensive suits or sensors.
AI is clearly a useful tool, although ethical considerations and technical limitations mean it can’t yet replace professionally-produced 3D animation.
What are the ethical considerations surrounding AI-powered production?
When using AI tools for your video production, innovation agencies like Rock Paper Reality can help you consider important concerns including brand safety and copyright ownership.
References
- https://www.thedrum.com/opinion/2022/03/16/3-things-brands-need-know-about-gen-z-s-cx-expectations
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/jefffromm/2023/03/16/gen-z-is-impacting-customer-experience-forrester-gartner-experience-dynamic-execs-share-insights/
- https://www.precedenceresearch.com/immersive-technology-market
- https://rockpaperreality.com/insights/ar-use-cases/rock-paper-reality-partners-with-chronic-cellars-to-bring-first-of-its-kind-personalized-ar-sommelier-to-life/